Utility Vegetation Management: Ensuring Safety and Reliability for Critical Infrastructure
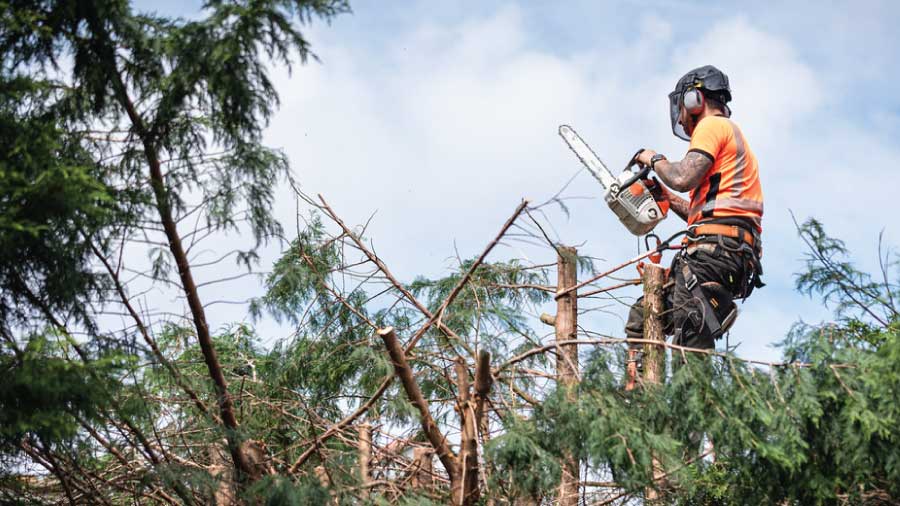
Utility companies face the constant challenge of managing vegetation near power lines and other critical infrastructure. Overgrown trees and vegetation can cause power outages, spark wildfires, and result in regulatory fines, making proactive management essential. Utility Vegetation Management (UVM) focuses on maintaining safe clearance, minimizing risks, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
This article explores what utility vegetation management entails, why it is essential, the techniques used, and how advanced technologies are revolutionizing the way utilities approach vegetation management.
What is Utility Vegetation Management?
Utility Vegetation Management (UVM) is the process of monitoring, maintaining, and controlling vegetation growth around utility infrastructure such as power lines, substations, and pipelines. The goal of UVM is to ensure the reliability of energy distribution, reduce safety risks, and comply with federal and local regulations.
This practice is especially critical in regions prone to extreme weather events, where falling trees or overgrown vegetation can exacerbate hazards. UVM employs a combination of traditional and advanced methods, from manual inspections to cutting-edge technology.
Why Utility Vegetation Management is Crucial
- Preventing Power Outages
Vegetation is one of the leading causes of electrical outages. Proactively trimming and clearing vegetation near power lines helps maintain uninterrupted service. - Reducing Wildfire Risks
In dry and fire-prone regions, contact between vegetation and power lines can ignite catastrophic wildfires. UVM minimizes this risk through consistent maintenance. - Ensuring Safety
Falling trees or branches can damage infrastructure and pose risks to public safety. UVM mitigates these dangers by addressing hazardous vegetation proactively. - Regulatory Compliance
Federal and local regulations mandate utility companies to maintain vegetation near their assets. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal consequences. - Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
Reliable power delivery and reduced service interruptions translate into higher customer trust and satisfaction.
Techniques in Utility Vegetation Management
Utility companies employ a variety of techniques to manage vegetation effectively:
1. Routine Inspections
Regular inspections identify at-risk vegetation before it causes problems. This includes visual inspections by field crews and advanced methods like aerial surveys.
2. Mechanical Trimming
Specialized equipment, such as bucket trucks and tree-trimming machines, is used to cut back vegetation and maintain safe clearances around power lines.
3. Herbicide Application
Selective use of herbicides controls vegetation growth while minimizing environmental impact. This technique is particularly effective for managing invasive species.
4. Integrated Vegetation Management (IVM)
IVM combines mechanical, chemical, and biological methods to manage vegetation sustainably. This approach balances safety with environmental stewardship.
5. Remote Monitoring
Technologies like drones, LiDAR, and satellite imagery enable utilities to monitor vegetation growth over large areas without extensive field labor.
6. Predictive Maintenance
Advanced analytics predict vegetation growth patterns and potential risks, allowing utilities to schedule maintenance proactively.
The Role of Technology in Utility Vegetation Management
Technological advancements are transforming UVM by improving efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Key innovations include:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
LiDAR creates detailed 3D models of vegetation and utility infrastructure, helping teams identify risks and plan precise trimming activities. - Drones and UAVs
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors capture aerial images of vegetation, reducing inspection time and costs. - Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered software analyzes vegetation data to identify risks, predict growth patterns, and optimize maintenance schedules. - Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS maps integrate spatial data with vegetation insights, enabling utilities to visualize and prioritize areas requiring maintenance. - IoT Sensors
Internet of Things (IoT) devices monitor environmental factors such as soil moisture and vegetation health, providing real-time insights. - Mobile and Cloud Platforms
Cloud-based tools allow teams to collaborate seamlessly, while mobile applications provide field crews with real-time access to data and work orders.
Benefits of Proactive Utility Vegetation Management
- Enhanced Reliability
Proactive UVM minimizes outages and disruptions, ensuring a consistent supply of electricity to customers. - Cost Efficiency
Identifying and addressing risks early reduces emergency repairs and long-term maintenance costs. - Environmental Sustainability
Techniques like IVM promote biodiversity and minimize the environmental impact of vegetation control. - Improved Public Safety
Clearing hazardous vegetation prevents accidents, fires, and other safety risks. - Streamlined Operations
Leveraging technology streamlines workflows, allowing utilities to manage large service areas effectively.
Best Practices for Utility Vegetation Management
- Develop a Comprehensive Plan
A detailed UVM strategy should include risk assessment, scheduling, and resource allocation tailored to specific geographic and regulatory requirements. - Invest in Advanced Technology
Utilize tools like drones, LiDAR, and AI-driven analytics to enhance efficiency and accuracy. - Engage in Regular Training
Ensure field crews and managers are trained on the latest methods, tools, and safety protocols. - Promote Sustainable Practices
Adopt eco-friendly approaches such as selective trimming and planting native vegetation to balance operational needs with environmental responsibility. - Monitor and Adapt
Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of UVM strategies and adjust plans based on changing conditions or regulatory updates.
Real-World Applications of Utility Vegetation Management
- Wildfire Prevention in California
Utility companies in California have adopted AI and drone technology to monitor and manage vegetation in high-risk areas, significantly reducing wildfire incidents. - Hurricane Preparedness on the East Coast
By leveraging predictive analytics, utilities in hurricane-prone regions schedule vegetation clearance ahead of storm seasons, minimizing power outages. - Urban Tree Management
In densely populated areas, utilities use GIS mapping to manage vegetation near power lines while preserving urban greenery.
Conclusion
Utility Vegetation Management is a critical component of infrastructure safety and reliability. By adopting proactive strategies and leveraging modern technologies, utilities can reduce risks, ensure compliance, and enhance operational efficiency. UVM is not just about trimming trees—it’s about creating a resilient infrastructure that can withstand the challenges of modern demands and environmental change.
Is your utility ready to embrace the future of vegetation management? A robust UVM program is the key to protecting assets, ensuring public safety, and delivering reliable services.