Recovering A2L Refrigerants: What Technicians Need to Know
As the use of A2L refrigerants grows due to their lower global warming potential, HVAC technicians must stay informed on the proper handling and recovery of A2Ls. These mildly flammable refrigerants require specialized knowledge and equipment to ensure both safety and efficiency. Recovering A2Ls involves not only careful attention to safety protocols but also an understanding of the specific pressures and characteristics of A2Ls.
Whether retrofitting existing systems or performing routine maintenance, technicians need to be well-versed in the recovery of A2Ls to prevent leaks, reduce environmental impact, and comply with industry regulations. In this guide, we’ll explore key considerations that every HVAC technician should know when dealing with A2L refrigerants.
What are the refrigerant recovery methods?
Refrigerant recovery methods include passive recovery, which relies on the system’s pressure to transfer refrigerant, and active recovery, where a recovery machine extracts refrigerant, both essential for safe and efficient handling. Let’s see what’s essential to understand when it comes to A2Ls:
Understanding A2L refrigerants
A2L refrigerants, such as R-32 and R-1234yf, are gaining popularity due to their lower environmental impact. Unlike traditional options, A2Ls are mildly flammable, which requires technicians to adopt new methods and tools when working with them. Recovering A2Ls involves extracting the refrigerant from the system to either recycle, reclaim, or dispose of it in accordance with safety and environmental guidelines.
Key safety considerations
The mildly flammable nature of A2Ls demands heightened attention to safety protocols during recovery. Although they are less hazardous than highly flammable refrigerants, they still pose risks if mishandled. Technicians should ensure that proper ventilation is available in the recovery area to prevent the accumulation of gasses. If the concentration of A2L in the air reaches certain levels, it can create flammable conditions, so leak detection and monitoring are crucial.
Additionally, technicians should be equipped with personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and flame-resistant clothing when handling A2Ls. Electrical tools and components used in the process must be rated for use in mildly flammable environments to avoid igniting the refrigerant.
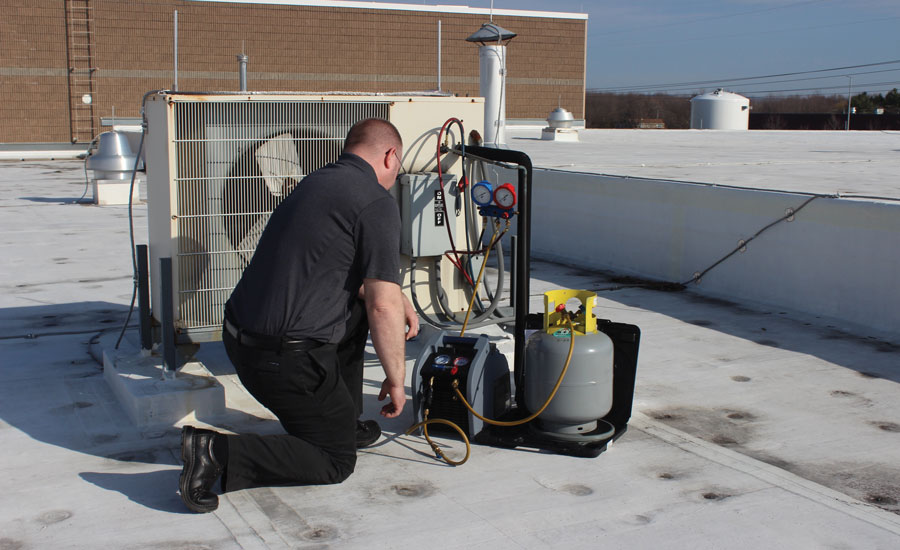
Recovery methods for A2L refrigerants
When recovering A2Ls, technicians typically use two main methods: passive recovery and active recovery.
- Passive recovery: This method relies on the system’s own pressure to transfer the refrigerant into the recovery tank. It is a slower process but can be suitable for small systems with lower refrigerant volumes. However, for A2Ls, passive recovery may not always be practical due to their pressure and flammability characteristics.
- Active recovery: This method uses a recovery machine to actively extract the refrigerant from the system. Active recovery is faster and more efficient, especially for larger systems. Recovery machines used for A2L refrigerants must be specifically designed or rated for handling mildly flammable gasses. Ensuring that the machine and recovery tanks are compatible with A2L refrigerants is vital to prevent leaks or accidents.
Using the right equipment
To safely recover A2Ls, technicians need specialized equipment that is certified for use with flammable refrigerants. This includes recovery machines, hoses, and tanks that are A2L compatible. Many recovery machines are now being designed with A2L refrigerant use in mind, providing technicians with the ability to handle them without the risk of ignition.
They should also use refrigerant scales and pressure gauges designed for A2Ls to accurately monitor the amount of refrigerant being recovered. Overfilling recovery tanks can be especially hazardous with A2Ls, so precise measurement is critical.
Training and certification
Technicians recovering A2Ls need proper training and certification. Recovery procedures for A2Ls differ from traditional refrigerants, so it’s essential that they are aware of the specific handling, storage, and safety requirements. Many organizations and HVAC associations offer A2L-specific certification programs, ensuring that technicians are equipped with the knowledge to safely recover these refrigerants.
Environmental compliance
Recovery of A2Ls not only ensures the safety of technicians but also protects the environment. By properly recovering and recycling them, technicians help reduce harmful emissions and comply with environmental regulations. A2Ls are designed to have a lower environmental impact, and proper recovery practices further contribute to global sustainability goals.