Implementing Predictive Maintenance with PLC and HMI Systems
In today’s industrial landscape, predictive maintenance has emerged as a crucial strategy for optimizing equipment performance and minimizing downtime. By leveraging advanced technologies, companies can anticipate failures before they occur, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. One of the key enablers of predictive maintenance is the integration of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems. This article explores how these technologies, including specific components like the XP502 Control Module and the 1769-PA4 A Power Supply, play a vital role in implementing predictive maintenance strategies.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance involves monitoring the condition of equipment and systems through real-time data analysis to predict and prevent potential failures. Unlike reactive maintenance, which addresses issues after they occur, or preventive maintenance, which schedules routine checks, predictive maintenance uses data-driven insights to address problems proactively. This approach not only extends the lifespan of machinery but also optimizes maintenance schedules and reduces unnecessary interventions.
Role of PLCs in Predictive Maintenance
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are critical in managing and automating industrial processes. They are designed to monitor and control various aspects of manufacturing systems. In the context of predictive maintenance, PLCs offer several key functionalities:
- Real-Time Data Collection: PLCs can gather data from various sensors and equipment, providing a continuous stream of information about the system’s health. This data is essential for analyzing performance trends and detecting anomalies.
- Data Processing: Advanced PLCs, such as those integrated with the XP502 Control Module, can process large volumes of data. The XP502 is known for its robustness and reliability, making it an ideal choice for complex automation tasks. It can handle sophisticated algorithms that are crucial for predictive maintenance, such as vibration analysis or temperature monitoring.
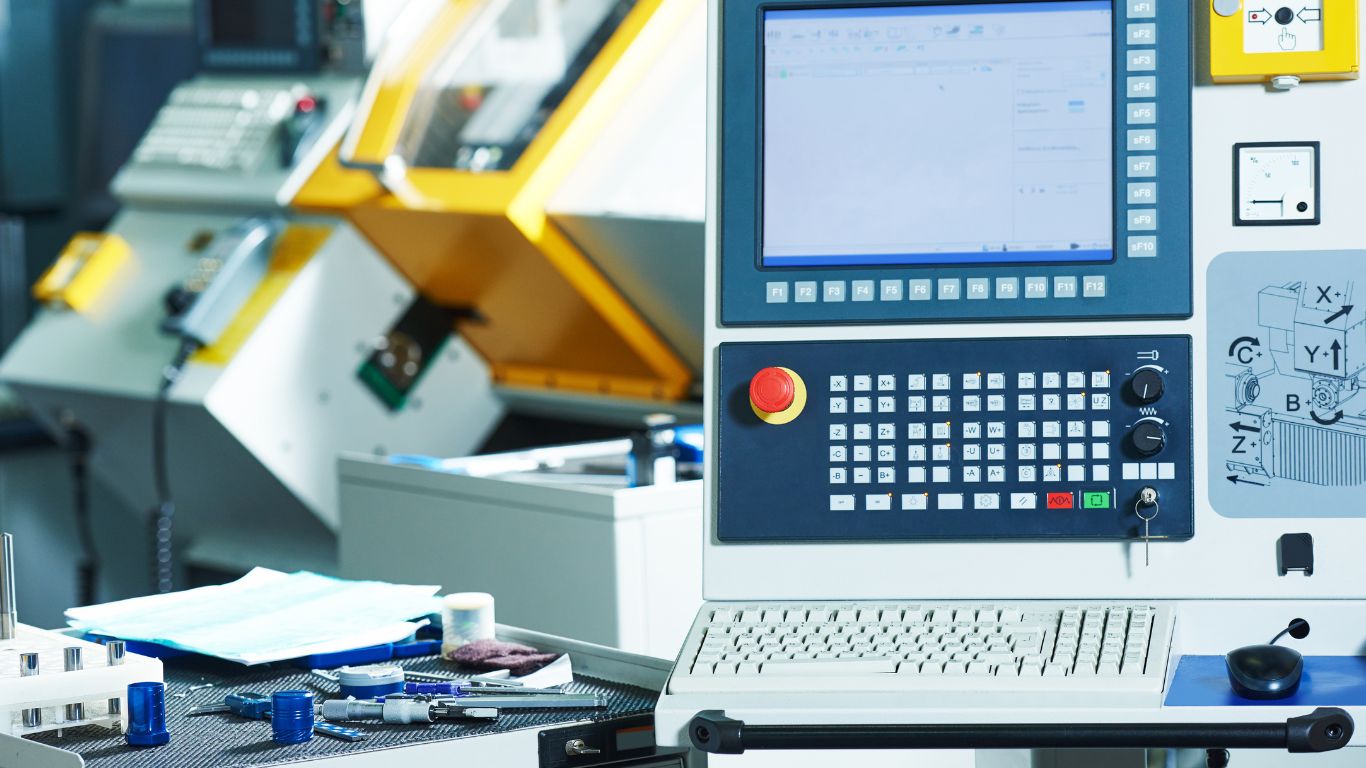
- Integration with HMI Systems: PLCs work in tandem with HMI systems to provide a user-friendly interface for monitoring and control. The data collected by the PLC is visualized through the HMI, enabling operators to make informed decisions quickly.
Importance of HMI Systems
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems play a pivotal role in predictive maintenance by offering a visual representation of data and allowing for intuitive interaction with the control system. Here’s how HMI systems contribute to predictive maintenance:
- Visualization of Data: HMIs display real-time data from PLCs in an easily understandable format. This includes graphical representations of equipment status, performance metrics, and alert notifications. Effective visualization helps operators quickly identify potential issues and assess the system’s overall health.
- Trend Analysis: Through HMI systems, operators can access historical data and trends, which are crucial for predictive maintenance. Analyzing past performance helps in understanding patterns and predicting future failures.
- Alerts and Notifications: HMIs are equipped to generate alerts and notifications based on the data received from PLCs. For instance, if a sensor detects an anomaly, the HMI can immediately notify the operator, allowing for timely intervention.
Integration of Control Module and Power Supply
The XP502 Control Module and the 1769-PA4 A Power Supply are integral components in implementing predictive maintenance strategies. Here’s how they contribute to the system:
- XP502 Control Module: The XP502 is a versatile control module designed for high-performance applications. Its capabilities include handling complex control tasks and integrating with various sensors and actuators. This module supports advanced predictive maintenance algorithms and ensures reliable data acquisition and processing. Its robustness ensures that the system remains operational even in demanding environments.
- 1769-PA4 A Power Supply: The 1769-PA4 A Power Supply is essential for providing stable and reliable power to PLC systems. In predictive maintenance, consistent power supply is critical for ensuring that PLCs and HMIs function correctly without interruptions. This power supply unit supports the smooth operation of control modules and sensors, thereby maintaining the integrity of data collection and processing.
Implementing Predictive Maintenance:
- System Assessment: Evaluate existing equipment and systems to determine the need for predictive maintenance. Identify critical components and potential failure points.
- Integration of PLC and HMI Systems: Install PLCs equipped with the XP502 Control Module and ensure reliable power supply with the 1769-PA4 A Power Supply. Integrate these with HMI systems for effective data visualization and control.
- Sensor Installation: Deploy sensors to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, vibration, and pressure. Connect these sensors to the PLCs for real-time data collection.
- Data Analysis: Utilize the PLC’s processing capabilities to analyze data and detect patterns indicative of potential failures. Implement predictive algorithms to forecast maintenance needs.
- Visualization and Alerts: Configure the HMI system to display relevant data and generate alerts based on predictive analysis. Ensure that operators are trained to interpret the data and respond to notifications effectively.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update predictive maintenance strategies based on performance data and evolving technologies. Ensure that the system adapts to changing operational conditions and improves over time.
Conclusion
Implementing predictive maintenance with PLC and HMI systems, supported by components like the XP502 Control Module and the 1769-PA4 A Power Supply, can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of industrial operations. By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, businesses can anticipate equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and ultimately achieve greater operational excellence. The integration of these technologies not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of critical assets, leading to substantial cost savings and improved productivity.