What Are the Different Types of Bed Rails Available for Those with Mobility Issues?
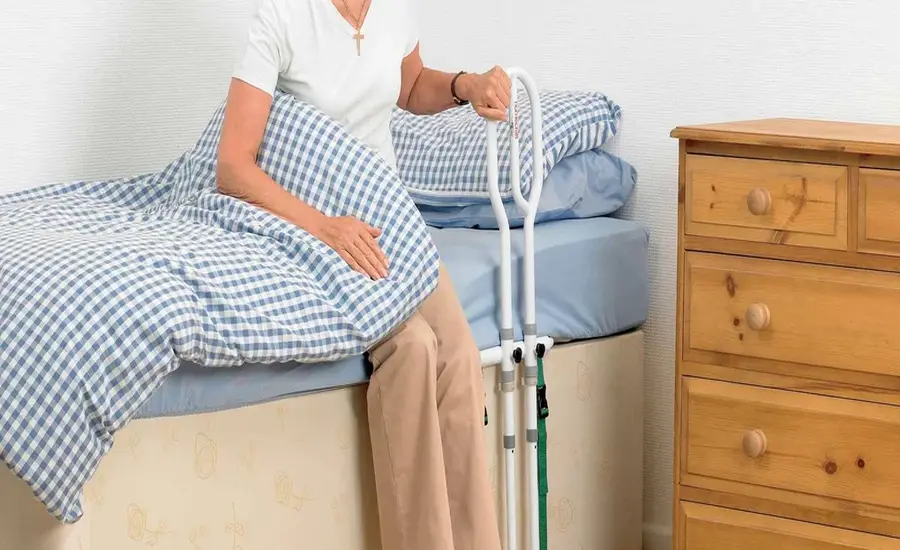
When selecting bed rails for individuals with mobility issues, understanding the various types available is crucial for ensuring safety, comfort, and functionality. Bed rails come in a range of designs, each catering to different needs and bed configurations. Here are the different types of bed rails that can help individuals with mobility challenges:
1. Standard Bed Rails
Standard bed rails are widely used and designed to provide basic support and prevent falls. They are typically installed along the side of the bed and can either be fixed or adjustable.
Features:
- Fixed Length: These rails have a fixed length and height, suitable for standard bed sizes.
- Material: Made from durable materials such as metal or heavy-duty plastic, ensuring stability.
- Installation: Usually attach directly to the bed frame and do not require complex installation.
Pros:
- Simplicity: Easy to install and use.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than other types of bed rails.
Cons:
- Limited Adjustability: Fixed rails do not offer flexibility in height or length.
- Potential Obstruction: May obstruct access to the bed if not positioned correctly.
2. Adjustable Bed Rails
Adjustable bed rails offer flexibility in terms of height, length, and sometimes angle. They are ideal for users who need customization to fit their specific needs.
Features:
- Height Adjustment: Allows users to adjust the height of the rail above the mattress, which can be useful for different bed heights.
- Length Adjustment: Some models offer adjustable length to fit various bed sizes.
- Material: Typically made from metal or robust plastic, with mechanisms for adjustment.
Pros:
- Customization: Can be tailored to fit different bed sizes and heights.
- Versatility: Suitable for a range of mobility needs and bed configurations.
Cons:
- Complexity: May require more effort to install and adjust.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than fixed bed rails.
3. Fold-Down Bed Rails
Fold-down bed rails can be folded down or out of the way when not needed. They offer convenience and flexibility for users who need occasional support but want to free up space when the rail is not in use.
Features:
- Foldable Design: Can be folded down to create more space or make it easier to access the bed.
- Material: Often made from durable metal or reinforced plastic.
- Installation: Typically mounts to the bed frame or the side of the mattress.
Pros:
- Space-Saving: Can be folded away to provide unobstructed access.
- Convenience: Useful for users who need support only at certain times.
Cons:
- Durability: Folding mechanisms may wear out over time.
- Complexity: May be more complex to install and adjust compared to fixed rails.
4. Bed Rails with Padded or Contoured Designs
Bed rails with padded or contoured designs focus on user comfort and safety by adding cushioning or ergonomic features to the rail.
Features:
- Padding: Soft padding or cushioning to prevent injury from accidental bumps.
- Contoured Shape: Ergonomically designed to fit the user’s body and reduce pressure points.
- Material: Often made with a combination of metal and foam or fabric coverings.
Pros:
- Comfort: Reduces discomfort and the risk of injury from hard surfaces.
- Safety: Provides additional protection against falls and accidental bumps.
Cons:
- Maintenance: Padded surfaces may require regular cleaning and maintenance.
- Cost: Typically more expensive due to additional features.
5. Bed Rails for Adjustable Beds
Bed rails designed specifically for adjustable beds accommodate the unique movement and positioning of these beds.
Features:
- Compatibility: Designed to work with the articulation of adjustable beds.
- Adjustable Angles: May allow adjustment to fit various positions of the bed.
- Material: Often made from durable metal or plastic.
Pros:
- Functionality: Compatible with the movement and adjustment of the bed.
- Support: Provides safety and support tailored to the adjustable bed’s range of motion.
Cons:
- Cost: May be more expensive due to specialized design.
- Complexity: Requires proper installation and adjustment for compatibility with the adjustable bed.
6. Floor-to-Ceiling Bed Rails
Floor-to-ceiling bed rails extend from the floor to the ceiling, providing a sturdy support system that can aid in transfers and movements.
Features:
- Height: Extends from the floor up to the ceiling, offering strong support.
- Material: Often made from metal or reinforced plastic.
- Installation: Requires secure anchoring to both the floor and ceiling.
Pros:
- Stability: Provides a robust support system for individuals needing significant assistance.
- Safety: Helps prevent falls and supports safe transfers.
Cons:
- Installation: Requires professional installation and may not be suitable for all room configurations.
- Cost: Generally more expensive due to the complexity of the installation.
7. Portable Bed Rails
Portable bed rails are designed to be easily moved and used in different locations. They are ideal for those who need temporary or multi-location support.
Features:
- Lightweight: Typically made from lightweight materials for easy transport.
- Portable Design: Can be easily moved and repositioned as needed.
- Material: Often made from collapsible metal or plastic.
Pros:
- Flexibility: Can be used in various locations or for travel.
- Convenience: Easy to set up and use in different settings.
Cons:
- Durability: May not be as robust as permanently installed rails.
- Support: May offer less support compared to fixed or adjustable models.
Final Words:
The right type of bed rail depends on individual mobility needs, bed configuration, and personal preferences. Whether opting for fixed, adjustable, fold-down, padded, or specialized bed rails, it’s important to consider factors such as safety, ease of use, and comfort. Consulting with healthcare professionals and evaluating specific requirements will help ensure the selection of the most suitable bed rail for enhancing safety and mobility at home.